wget https://cf-courses-data.s3.us.cloud-object-storage.appdomain.cloud/IBM-DB0231EN-SkillsNetwork/labs/Final%20Assignment/billingdata.sql
# verify download
ls
# Start MySQL then open mysql cli
$ sudo systemctl start mysql
$ sudo mysql -u root -pServer Performance - MySQL
Scenario
For this project you will assume the role of database administrator at a data analytics consulting company, and you’re in charge of the MySQL server. You will work with MySQL server and perform the tasks like configuration check, recovery of data. You will use indexing to improve the database performance. You will identify which storage engines are supported by the server and which table uses which storage engine. Optionally you will also automate backup tasks.
Project
Let’s pretend you’re the DBA so you’ll need to perform the following tasks of Database Administration on the MySQL server:
Tasks
- Installation & Provisioning
- Configuration
- Recovery
- Indexing
- Storage Engines
- Automation of routine tasks
Setup
We will be using an open-source cloud IDE platform to access the MySQL database which is running in a Docker container.
Restore db from Backup
Let’s suppose we already had a backup of our db saved, and an event caused us to have to restore all the data from it
Download sql Script
- Create db billing
- Connect to billing
- Restore billing using the sql file we downloaded
- List all the tables to make sure all are there
Show dbs
List Tables
- Show databases
- List Tables
# Create & populate db from sql script
mysql> source billingdata.sql
Query OK, 1 row affected (0.01 sec)
Database changed
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.05 sec)
Query OK, 132000 rows affected (2.02 sec)
Records: 132000 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> SHOW DATABASES;
+--------------------+
| Database |
+--------------------+
| billing |
| employees |
| employeesdb |
| information_schema |
| mysql |
| performance_schema |
| sys |
| world |
+--------------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
mysql> USE billing;
Database changed
mysql> SHOW TABLES;
+-------------------+
| Tables_in_billing |
+-------------------+
| billdata |
+-------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)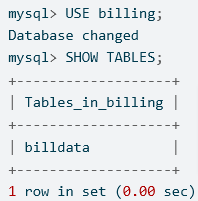
Find Table Data Size
What’s the size of the table: billdata
mysql> SELECT table_name, (data_length + index_length)/1024 FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE table_name = 'billdata';
+------------+-----------------------------------+
| TABLE_NAME | (data_length + index_length)/1024 |
+------------+-----------------------------------+
| billdata | 6672.0000 |
+------------+-----------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.03 sec)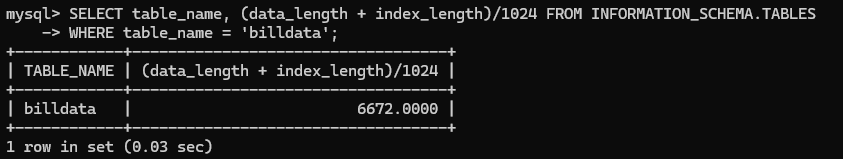
Indexing
Baseline Query Performance
- Let’s establish the baseline performance of a query
- Write a query to select
All rows with a billedamount > 19999in table billdata
mysql> SELECT * FROM billdata WHERE billedamount > 19999;
+--------+------------+--------------+---------+
| billid | customerid | billedamount | monthid |
+--------+------------+--------------+---------+
| 8509 | 285 | 20000 | 20096 |
| 68268 | 559 | 20000 | 20146 |
| 81622 | 643 | 20000 | 20157 |
| 84858 | 317 | 20000 | 20161 |
| 89353 | 871 | 20000 | 20163 |
| 102682 | 937 | 20000 | 20174 |
| 109574 | 386 | 20000 | 201810 |
| 121844 | 777 | 20000 | 201910 |
+--------+------------+--------------+---------+
8 rows in set (0.08 sec)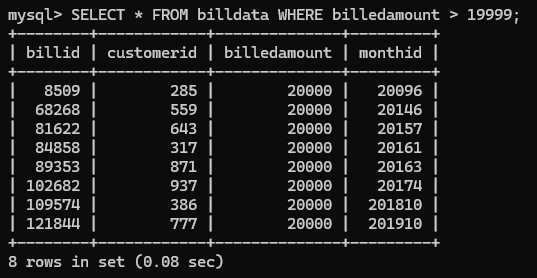
Explain
Let’s look at the details of the query to see how many rows were scanned
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM billdata WHERE billedamount > 19999; +----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ | id | select_type | table | partitions | type | possible_keys | key | key_len | ref | rows | filtered | Extra | +----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ | 1 | SIMPLE | billdata | NULL | ALL | NULL | NULL | NULL | NULL | 132130 | 33.33 | Using where | +----+-------------+----------+------------+------+---------------+------+---------+------+--------+----------+-------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.00 sec) # Let's look at the extisting index list mysql> SHOW INDEX FROM billdata; Empty set (0.01 sec)
Create an Index
- In order to attempt on improving the execution time of the query above
- Create an index to make it run faster
- We notice from above no index exists
mysql> CREATE INDEX billedamount_index ON billdata(billedamount);
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.50 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0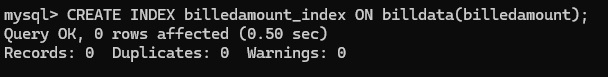
Test Performance Improvements
- Test again and see if creating an index had any impact on query performance
- Re-run the query above and compare
mysql> SELECT * FROM billdata WHERE billedamount > 19999;
+--------+------------+--------------+---------+
| billid | customerid | billedamount | monthid |
+--------+------------+--------------+---------+
| 8509 | 285 | 20000 | 20096 |
| 68268 | 559 | 20000 | 20146 |
| 81622 | 643 | 20000 | 20157 |
| 84858 | 317 | 20000 | 20161 |
| 89353 | 871 | 20000 | 20163 |
| 102682 | 937 | 20000 | 20174 |
| 109574 | 386 | 20000 | 201810 |
| 121844 | 777 | 20000 | 201910 |
+--------+------------+--------------+---------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)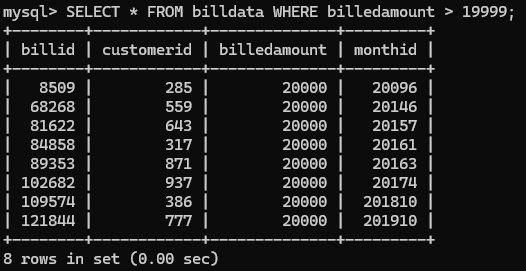
Explain
- Let’s see how many rows were scanned after adding an index
- As you can see only 8 rows were scanned??!!
mysql> EXPLAIN SELECT * FROM billdata WHERE billedamount > 19999;
Storage Engines
Find Supported Engines
- Run a command to find out if this MySQL server supports the MyISAM storage engine
mysql> SHOW ENGINES;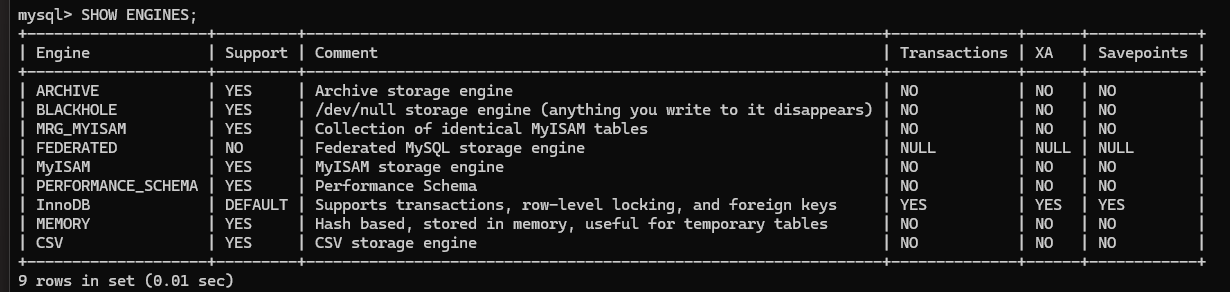
Storage Engine of Table
- Find the storage engine of the table billdata
mysql> SELECT table_name, ENGINE FROM INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES WHERE table_name = 'billdata';
+------------+--------+
| TABLE_NAME | ENGINE |
+------------+--------+
| billdata | InnoDB |
+------------+--------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)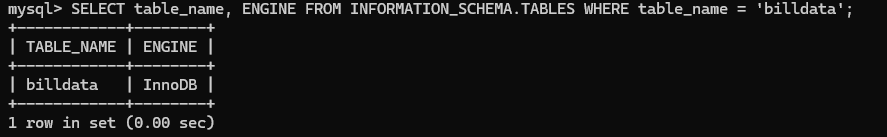
Task Automation
Backup Bash Script
Bash script to Backup all dbs
Write a bash script named mybackup.shthat performs the following tasks.
- Perform the backup of all databases using the mysqldump
- Store the output in the file all-databases-backup.sql
- In the /tmp directory, create a directory named after current date like YYYYMMDD. For example, 20210830
- Move the file all-databases-backup.sql to
/tmp/mysqldumps/<current date>/directory
mysqldump is a command line tool that performs logical backups of a database.
Its generic syntax is mysqldump db_name > backup-file.sql
Its extended syntax is mysqldump --all-databases --user=root --password=NzA4Ny1y > backup-file.sql